Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
LY Corporation (the “Company”) conducts risk management activities centered on Enterprise Risk Management (ERM), risk intelligence, incident tracking across the LY Corporation Group (the “Group”), and the development of a risk-conscious culture, all aimed at minimizing risks.
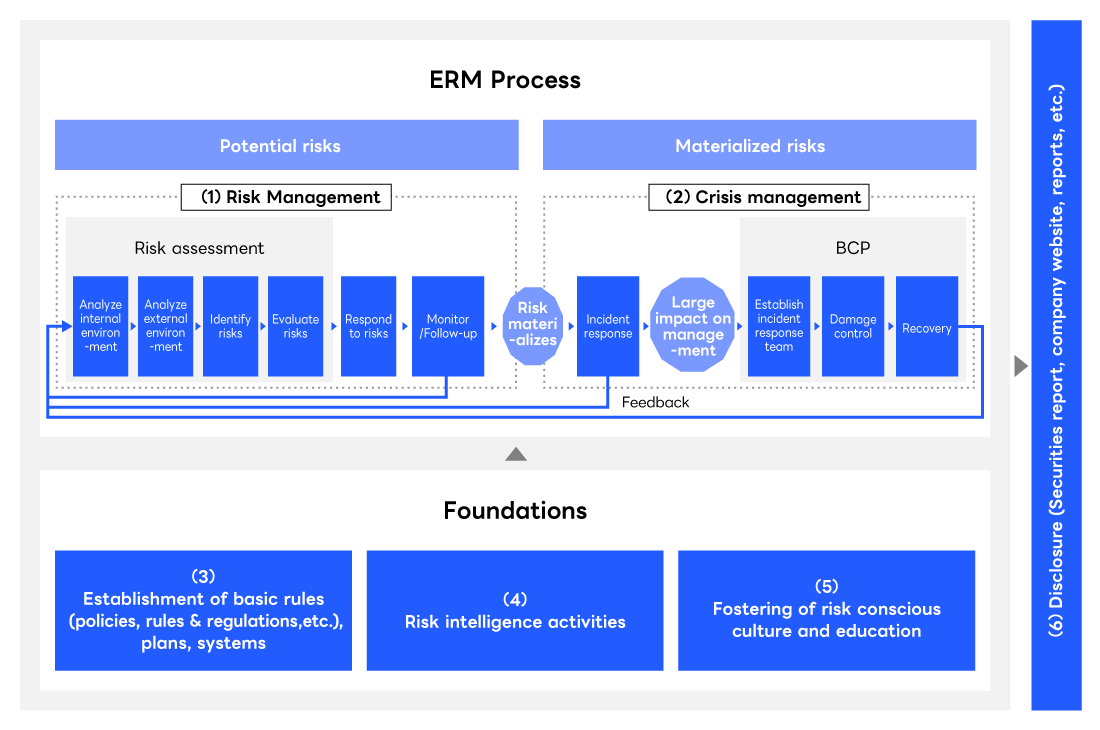
ERM Process and Process Infrastructure
In accordance with the regulations on ERM, LY Corporation comprehensively identifies and assesses risks related to the management and businesses of the Company and its Group companies, and promotes ERM activities that lead to the generation of corporate value. The Risk Management Committee convenes to make decisions related to risks.
(1) Risk management: The Company identifies risks and opportunities that could affect its achievement of the Group’s mission and business goals and then analyzes these from two angles: (i) how severe the impact would be if the risk materializes (i.e., how much it would affect the Company’s ability to achieve its goals), and (ii) the likelihood of the risk materializing (i.e., how likely and frequently it would occur). From this, the Company assesses the risk level based on impact × likelihood and prepares measures accordingly. At the end of the fiscal period, the Company reviews its responses and conducts a risk management maturity assessment with each division responsible for risk management and business division to understand the current situation and strive for improvements in the next fiscal year. Additionally, the Company analyzes both internal environments (self-analysis by each division responsible for risk management and business division) and external environments (information acquisition from external sources). Based on these analyses as well as insights from the top management and the persons in charge, the Company identifies particularly critical risks as the top risks of the LY Corporation Group. While bearing in mind the impact from the environment surrounding the Group, the Company reviews these top risks as needed, ranks them by priority level, and carries out and monitors the progress of measures.
(2) Crisis management: In the event of an incident, the Company takes prompt and appropriate initial actions to prevent the situation from escalating and to quickly bring it under control, and considers measures to prevent recurrence. Additionally, to ensure that users can continuously access essential services that serve as critical infrastructure for daily life and business, the Company has established a service continuity framework for emergencies.
(3) Establishment of basic rules, plans and systems: The Company establishes policies, rules, regulations, and others to support the operation of ERM processes.
(4) Risk intelligence activities: The Company collects and analyzes external information on matters such as the business environment and changes in social conditions, and shares the information with those engaged in risk management throughout the Group.
(5) Fostering risk conscious culture and education: The Company communicates the importance of risk management as a top message to all employees. Additionally, it uses all available channels to raise awareness on risk management throughout the Group so that all personnel can engage in their daily activities with risk management in mind.
(6) Information disclosure: The Company discloses the material risks of the LY Corporation Group and the status of its efforts to address them in a timely and appropriate manner through available channels.
ERM Structure
LY Corporation establishes an ERM structure, designating the highest responsibilities to the President and Representative Director, and strives to reduce and prevent risks by smoothly implementing an ERM process. The ISO31000 framework is used as an external guiding standard.
The Board of Directors determines the basic policies on risk management applicable to the entire Group. Based on the basic policies determined by the Board, executive bodies such as the Risk Management Committee, the Supervisory Organization of Risk Management (headed by the Head of the Governance Group), divisions responsible for risk management, and business divisions, develop the ERM structure and promote Group-wide risk management activities in cooperation with the Group companies.
In order to promptly respond to risks in an ever-changing business environment, important matters are reported to and discussed in the Top Management Committee (a meeting body comprising the President and Representative Director, directors, and others) and other relevant bodies. In addition, senior general managers are responsible for risks arising from the fields supervised by each business division head, and RM (Risk Management) Promotion Managers are also appointed to ensure a prompt response to risks. The Audit and Supervisory Committee, composed entirely of independent outside directors, and the internal audit division, led by the Head of the Internal Audit Group, maintain an independent structure to provide assurance and advise on the effectiveness of the risk management function. Reports on particularly noteworthy issues are provided to the Audit and Supervisory Committee as needed.
Furthermore, the function overseeing risk management is structurally separated from the business divisions to ensure independence. To further strengthen this independence, the Head of the Governance Group, who is responsible for the Supervisory Organization of Risk Management, and the Head of the Internal Audit Group, who is responsible for the internal audit division, are each held by different officials.
Related Links

*1 The Risk Management Committee is chaired by the President and Representative Director (the Chief Executive of Risk Management) and its members comprise directors (excluding outside directors) who serve as Committee members, the CFO and CTO, and the Head of the Governance Group (responsible for supervising risks), as well as personnel appointed by the Chief Executive of Risk Management, and the corporate officer in charge of the Supervisory Organization of Risk Management. The Committee supervises the risk management of the entire Group.
Risk Categories
LY Corporation defines risk categories to thoroughly understand the risks faced by the LY Corporation Group. The Company classifies risks within specific fields as risk categories and designates the divisions in charge of each risk category to conduct risk assessments. When a top risk is identified from among the risk categories, the division in charge of the risk category also becomes the risk owner.
| Classification | Risk Categories | Outline | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic risks | Business strategy risks | Risks affecting or arising from the organization's business strategy and strategic objectives | |
| Non-strategic risks | Finance | Market risks | Risks of financial impact from fluctuations in various market risk factors |
| Credit risks | Risks of incurring financial losses due to the deterioration of financial conditions of credit recipients | ||
| Liquidity risks | Risks of not being able to secure necessary funds, inhibiting cash management, or risks of being forced to raise funds at an interest rate significantly higher than usual | ||
| Investment | Investment risks | Risks of being affected by fluctuations in the value of invested assets in inter-company investments/loans and M&As | |
| Information technology | System operational risks | Risks of incurring losses due to errors, system downtime, malfunctions, or inadequacies in operations necessary for the running and maintenance of services | |
| Product quality risks | Risks of affecting users due to lack of quality control in the services and products provided | ||
| Information security risks | Risks of damage due to break down, corruption, or falsification of information systems or data, or information leakage, etc. | ||
| Legal/compliance | Legal risks | Risks of being affected by penalties and damage compensations resulting from non-compliance with or breach of contracts for various transactions, etc., and risks of the companies and employees of the LY Corporation Group violating laws and regulations | |
| Compliance risks | Risks of being affected by actions that violate the LY Corporation Group Code of Conduct or internal regulations, risks of the Group or its employees committing violations intentionally or due to gross negligence | ||
| Money laundering and financing of terrorism risks | Risks of the LY Corporation Group’s services being misused for money laundering or for financing terrorism, or risks of being warned by supervisory authorities for insufficiencies in anti-money laundering measures | ||
| Governance | Corporate governance risks | Risks that insufficiently established governance frameworks for important decision-making in the LY Corporation Group lead to inability of the Group to make timely and appropriate decisions | |
| Data governance risks | Risks associated with the management and use of retained data | ||
| Supply chain governance risks | Risks of being affected by the inappropriate selection of subcontractors or inadequate management of subcontract work and subcontract employees | ||
| Social | Economic security risks | Risks of being affected by changes in political, economic, and social climates in specific countries and regions related to businesses | |
| Regulatory/public policy risks | Inadequacies related to understanding of regulations, policies, stakeholder conditions, etc.; risks related to insufficient response to the various laws and regulations | ||
| Environmental/social risks | Risks of businesses adversely affecting the environment or society, or risks of businesses being affected by external social environment | ||
| Reputation risks | Risks of being affected by the spreading of bad reputations or rumors, or risks of failing to respond to the media | ||
| Business operation | Business continuity risks | Risks of difficulty in continuing to operate businesses or services due to natural disasters or other external factors | |
| Human risks | Risks related to human resources, or risks that threaten the life/health of employees | ||
| Business operations risks | Risks of incurring losses due to clerical errors in business operations | ||
| Other | Tangible asset risks | Risks of losses due to damage to tangible assets or deterioration in the quality of work environment | |
Fostering Risk Conscious Culture within the LY Corporation Group
LY Corporation regularly conducts (one or more times a year) mandatory training for all employees to learn the basic knowledge and concepts of risk management necessary to perform their work and to raise their awareness. The Company also gathers risk-related proposals and information from internal and external experts in various fields and notifies all employees of these.
The Company also believes that building relationships that facilitate the sharing of important information and communication among the Group companies is an important aspect of risk management of the Group. The Company is therefore committed to communication with each Group company and regularly shares information with the risk management staff of each company.
Risk management activities are promoted through mutual sharing of information on matters such as the Company’s initiatives and other information from each Group company.
In addition, risk intelligence seminars and other activities open to all personnel from the Group are held to raise risk management awareness throughout the Group.
Risk Management in Service Planning and Development
LY Corporation examines risks during service planning and development in accordance with its business characteristics.
For example, the Company introduces guidelines that clearly define the process for developing and operating products. At PayPay Corporation, a Group company, each department conducts risk identification, risk assessment, and control evaluation, and the company has introduced a process in which the frontline itself develops a risk response plan if the residual risks are unacceptable.
Top Risks of the LY Corporation Group
From its risk management activities, the Company selects the top risks for the LY Corporation Group, which serve as a guideline for the risk management activities of the entire Group.
Top risks are identified one or more times a year after the Risk Management Committee discusses risks that could have significant impact on the LY Corporation Group. Important risks identified during the fiscal year are reported to the Top Management Committee and decisions are made as they arise. The Risk Management Committee also convenes as needed in addition to their regular meetings.
Risk owners are appointed for top risks in order to clarify the responsibilities over the response measures. The risk owners promote the matters decided by the Top Management Committee and other bodies regarding priorities and response policies, and report the status of their response to the Risk Management Committee once every six months.
After the reports on risk management are submitted to the Risk Management Committee, the details are also reported to the outside directors by the Supervisory Organization of Risk Management at the Board of Directors meetings.
A structure is in place and is implemented so that the Supervisory Organization of Risk Management can regularly monitor the implementation status of risk management.
FY2025 Top Risks of the LY Corporation Group
LY Corporation defines risk categories to thoroughly understand the risks faced by the LY Corporation Group. The Company classifies risks within specific fields as risk categories and designates the divisions in charge of each risk category to conduct risk assessments. When a top risk is identified from among the risk categories, the division in charge of the risk category also becomes the risk owner.
- Business strategy risks
- Information security risks
- Geopolitical/economic security risks
- Regulatory/public policy risks
Please refer to the Annual Securities Reports (currently available in Japanese only) for financial risks that may have material impacts on investors' investment decisions.
| Top risk categories | Representative risk contents | Measures to mitigate risks |
|---|---|---|
| Business strategy risks | ||
| Impact of delays in responding to generative AI technology |
|
|
| Stagnation of business advancement (organizational rigidity and decreased efficiency) |
|
|
| Information security risks | ||
| Risks related to cybersecurity |
|
|
| Risks related to specified user information |
|
|
| Risks related to data governance |
|
|
| Geopolitical/economic security risks | ||
| Risks related to economic security |
|
|
| Regulatory/public policy risks | ||
| Risk of corporate value deterioration due to increased regulations and reputational damage arising from the misuse of platforms and services |
|
|
Related Links
Emerging Risks
By regularly reviewing risks, the Company identifies and manages emerging risks that could significantly impact its business. The Company focuses on key risks identified annually and selects emerging risks for which it implements countermeasures.
The emerging risk that has been identified for FY2025 is the following:
Risks arising from the use of generative AI, particularly centered around AI agents
| Representative risk content | If the Company fails to appropriately respond to the rapid advancement of generative AI technology, the competitiveness of its core businesses, such as search and advertising, may decline, making value creation challenging. However, effectively leveraging generative AI technology can enable the creation of new value not only in these core areas but also across various service domains. |
|---|---|
| Impact on business | If the Company fails to achieve strategic outcomes from its engagement with generative AI technologies and becomes unilaterally dependent on external resources or specific corporations, it risks losing its competitive technological edge. However, successful strategic integration of generative AI can provide new user experiences in various service domains, elevate customer satisfaction, and secure a competitive advantage. |
| Countermeasures |
|
Critical Incident Response
The criteria for critical incidents are defined in the Rules on Incident Management. A system is in place to promptly report incidents which fall under critical incidents to the management via the Supervisory Organization of Risk Management. A system is also in place to ensure that the reported incidents are also shared with the divisions responsible for risk management, so that the status of the incidents within the Group can be promptly identified. Additionally, the Company has implemented the LY Corporation Group Critical Incident Reporting Guidelines , ensuring that any critical incidents occurring within Group companies are reported to management according to the same standards.
Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
LY Corporation provides numerous services that serve as infrastructures essential for daily lives and businesses. Many of these services play important roles in the event of a sudden accident/natural disaster, and the social responsibilities of the Company are increasing. The Company implements systems to minimize damages in the event of a disaster and to ensure that users have stable access to its services.
Continuance of Services in Emergencies
Especially at the time of emergencies, such as large-scale earthquakes, one of LY Corporation’s missions is to provide services needed by users, such as Yahoo! JAPAN News, disaster information, and the LINE communication app, without interruption.
To ensure that users can continue to access the services with peace of mind, the Company establishes a system to ensure the continuous operation of services at multiple locations in emergencies.
Flexible Work Systems Taking Emergencies into Account
LY Corporation introduces a work system that allows employees to work from home in a VPN environment with appropriate security measures in place.
While providing diverse and flexible work styles, as part of the BCP, this work style is designed to ensure the safety of employees and the continuity of business operations in the event of natural disasters or other situations that make it difficult for employees to commute or leave the house.
Establishment of Crisis Response Headquarters and Periodic Drills
In the event of an emergency, a Crisis Response Headquarters, led by the President and Representative Director will be established to ensure the continuity and early recovery of services.
LY Corporation formulates the BCP Rules that form the basis for the Crisis Response Headquarters, clarifies the roles of management and each department in the event of an emergency, gathers relevant personnel to conduct drills on the assumption of an emergency situation and safety confirmation drills for all employees on a regular basis, and reviews the BCP as needed in response to drill results and changes in the environment.